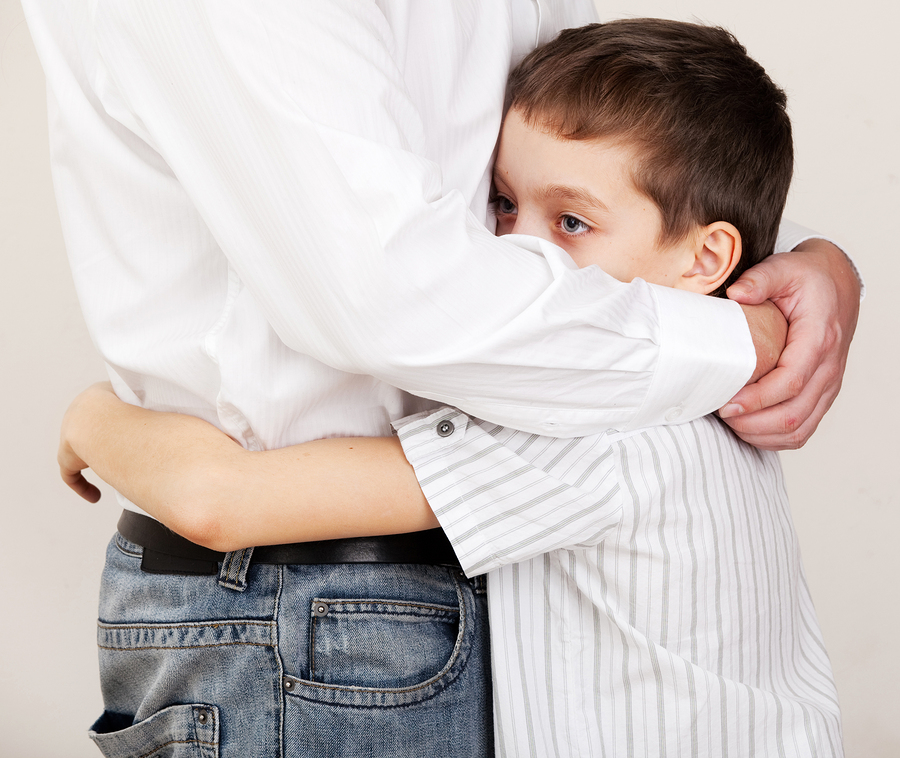
Unintentional injuries are thethird leading cause of death in the United States. These deaths cause significant emotional and financial suffering for those left behind, particularly when caused by someone else’s careless or reckless actions.
A fatality caused by someone else’s negligent or intentional actions is known as wrongful death. Of course, all deaths feel wrong to those left behind, but wrongful death has a specific meaning for wrongful death lawyers and their clients. A wrongful death gives legal rights to those left behind. In this blog post, we discuss those rights.
What Is a Wrongful Death Lawsuit?
Georgia law defines wrongful death as the death of a person caused by the “negligent, reckless, intentional, or criminal” acts of another person or entity (such as a business).Negligence is considered “a failure to behave with the level of care that someone of ordinary prudence would have exercised under the same circumstances.”
Normally, a person injured by someone else’s wrongful actions has rights under Georgia law to take legal action against the wrongdoer for damages. This is what is known as a personal injury lawsuit.
Wrongful death claims are similar to personal injury suits, but with the obvious difference that the person fatally injured cannot bring his or her own case to court. Instead, the law gives others the right to make that claim on behalf of the deceased.
Who Can File a Wrongful Death Lawsuit in Georgia?
Georgia law only allows certain people to file a wrongful death lawsuit.
Spouse of the Deceased
Thespouse of the deceased is the first person who can file a wrongful death suit. The spouse can also file the suit on behalf of any minor children of the deceased. Either way, the spouse is entitled to at least one-third of the full financial recovery from the wrongful death claim.
Children of the Deceased
If there is no surviving spouse, then the children of the deceased person can file a wrongful death claim.
Parents of the Deceased
If the deceased person does not have a surviving spouse or children, then his or her surviving parents may file a wrongful death lawsuit under Georgia law.
If the parents are separated or divorced, the division of any money recovered through the wrongful death action is within the court’s discretion. Also, if one of the parents abandoned or failed to provide for the deceased child, the law may bar that person from filing a wrongful death claim.
Estate Representative
The designated legal representative of the deceased’s estate may also file a wrongful death claim. In that case, the deceased person’s estate receives any money damages which have been awarded. A probate court then distributes the damages as required by law.
The Basics of a Wrongful Death Suit
According toGeorgia law, you can sue anyone legally liable for causing your loved one’s death negligently, recklessly, intentionally, or criminally. Wrongful death claims involve many types of fatal accidents and injuries. These include motor vehicle accidents, slip & fall accidents, defective products, and medical malpractice. To prevail, the party filing the suit must prove your case by a preponderance of the evidence.
There are several types of damages typically awarded in wrongful death cases. These include:
Full Value of Life Damages
It is extremely difficult to place a value on someone’s life. However, these damages try to do just that. They place a value on the life of a person based on both economic and non-economic factors. Here is how each of those factors is determined.
- Economic value. The economic factor pertains to the earnings capacity for the victim. How much money would the deceased have made had they lived to die a natural death? If the deceased was a working adult, it is relatively easy to calculate this figure based upon the deceased victim’s earnings, benefits, pension, expected time left in the workforce, and other pertinent factors. If the deceased was unemployed, retired, a stay-at-home parent, or a child, this amount is more difficult to calculate. However, these lives also have economic value. The court may consider evidence from expert witnesses to calculate a fair amount.
- Non-economic value. The non-economic component of these damages is much more subjective. The victim’s life was tragically cut short, so they lost all of the benefits of living a full life. Their loved ones lost the care, companionship, and other intangible benefits the deceased may have provided. Lawyers for the parties filing a wrongful death lawsuit collect extensive information about the deceased person to demonstrate the full impact of the loss.
Estate Claim
The estate of the deceased person must file the estate claim. It does not include the value of the life of the deceased. Instead, it only accounts for the expenses the estate may have had to pay because of the death, such as:
- Medical expenses;
- Funeral and burial expenses; and
- Pre-death pain and suffering endured by the deceased.
It is essential for survivors of a deceased person to keep records of any such expenses.
Punitive Damages
In rare cases, the judge awards punitive damages to punish the defendant. These are sometimes awarded in cases such as driving under the influence and other cases where the defendant intentionally harmed the deceased.
Time Limits on a Wrongful Death Claim
A statute of limitations is the time limit that a survivor or personal representative of the deceased person to bring a case of wrongful death to court.
Typically, there is a two-year statute of limitations from the time of the person’s death. If the claim is not filed in that two-year time limit, the possibility of bringing forth such a claim is almost always lost. There are exceptions to this rule. However, you should discuss the applicable time limits with your attorney.
No amount of money can give you back your loved one, but a wrongful death suit may help ease the financial consequences and deliver a measure of justice. Wrongful death claims can be very complex, so consult an experienced wrongful death lawyer to help take you through the process.